Types of Data in Machine Learning
Data refers to a collection of information, facts, or statistics that are typically stored and processed electronically. It can take many forms, including text, numbers, images, audio, or video, and is used for a variety of purposes, such as analysis, research, and decision-making. A data set is a collection of related information or records. The information may be on some entity or some subject area.
For example, we may have a data set on students in which each record consists of information about a specific student. Again, we can have a data set on student performance which has records providing performance, i.e. marks on the individual subjects.
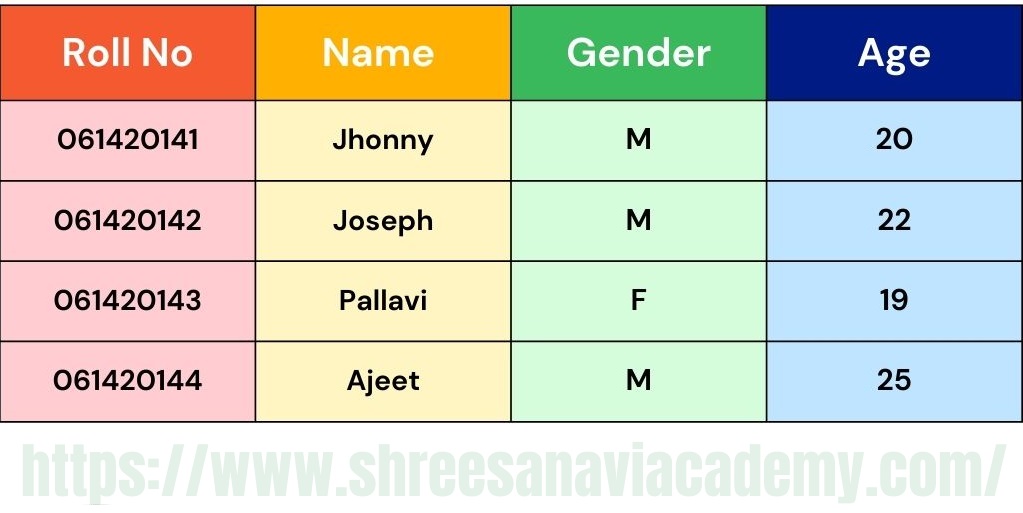
Student Data Set:
Student Performance Data Set:
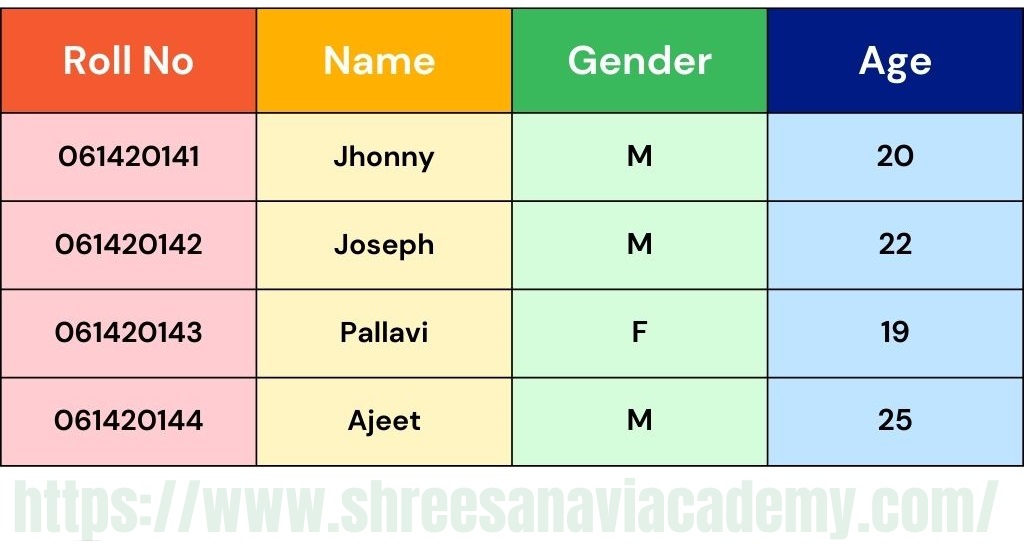
A record is a single row in a data set. Additionally, each data set contains a number of attributes, each of which provides details on a distinct characteristic. For example, there are four attributes—Gender, Roll Number, Name—in the student data set. Each of the student's ages, naturally, is a distinct characteristic of the student entity. Features, variables, dimensions, and fields are additional terms for attributes. Both the Student and Student Performance data sets have four features or dimensions, so it is specified that they should be stored in a four-dimensional data space. Since each row has a unique value for each of the four attributes or features, a row or record symbolises a point in the four-dimensional data space. It makes perfect sense that the value of an attribute can change from record to record.