Image Restoration
Restoration deals with improving the presence of the image. It is an objective approach because restoration techniques tend to be based on mathematical or probabilistic models of image processing. Restoration improves image in some predefined sense. It is an objective process. Restoration attempts to reconstruct an image that has been degraded by using a priori knowledge of the degradation phenomenon. These techniques are geared toward modeling the degradation and then applying the inverse process to recover the original image. Restoration techniques are based on mathematical or probabilistic image processing models. Enhancement, on the other hand, is based on human subjective preferences regarding what constitutes a "good" enhancement result. Image restoration refers to a class of methods that aim to remove or reduce degradations during the digital image acquisition process.
All natural images when displayed have gone through some degradation:
-
During display mode
-
During acquisition mode, or
-
During the processing mode
The degradation may be due to
-
Sensor noise
-
Blur due to camera misfocus
-
Relative object-camera motion
-
Random atmospheric turbulence
-
Others
Degradation Model:
The degradation process operates on a degradation function that operates on an input image with an additive noise term. The input image is represented by using the notation f(x,y), noise term can be represented as η(x,y). These two terms when combined give the result as g(x,y). If we are given g(x,y), some knowledge about the degradation function H or J and some knowledge about the additive noise teem η(x,y), the objective of restoration is to obtain an estimate f'(x,y) of the original image. We want the estimate to be as close as possible to the original image. The more we know about h and η, the closer f(x,y) will be to f'(x,y). If it is a linear position invariant process, then degraded image is given in the spatial domain by
g(x,y)=f(x,y)*h(x,y)+η(x,y)
h(x,y) is spatial representation of degradation function and symbol * represents convolution. In the frequency domain, we may write this equation as
G(u,v)=F(u,v)H(u,v)+N(u,v)
The terms in the capital letters are the Fourier Transform of the corresponding terms in the spatial domain.
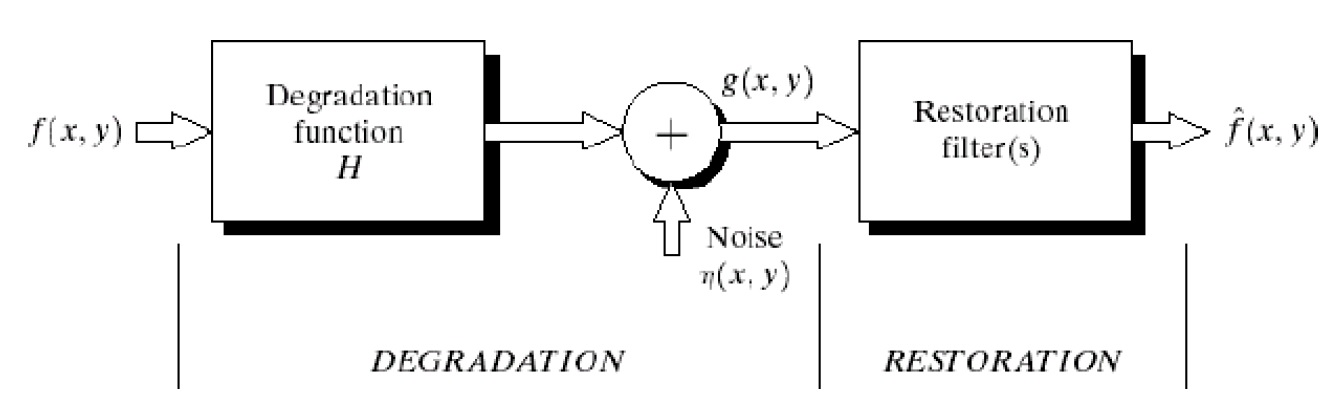
Fig: A model of the image Degradation / Restoration process