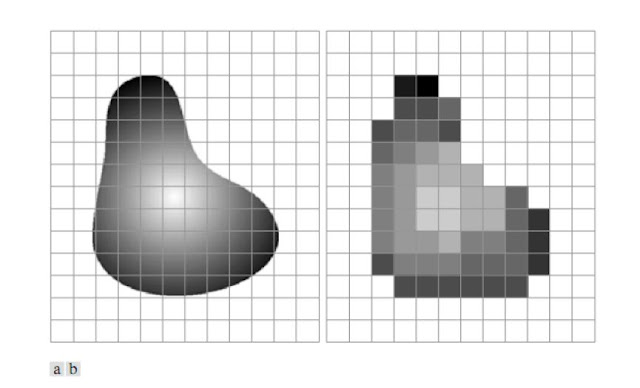
Digital Image Representation
An image can be defined as a two-dimensional function f(x, y), where x and y are spatial (plane) coordinates and the amplitude of f at any point (x, y) is called the intensity of the image at that point. The term gray level is used to refer the intensity of monochrome images. Color images are formed by a combination of individual 2-D images. For example, in the RGB color system, a color image consists of three (red, green, and blue) individual component images.
An image may be continuous with respect to the x and y-coordinates, and also in amplitude. Converting such an image to digital form requires that the coordinates as well as amplitude, be digitized. Digitizing the coordinate values is called sampling; digitizing the amplitude values is called quantization. Thus, when x, y, and the amplitude values of f are all finite, discrete quantities, we call the image a digital image.
Examples of digital images are:
-
Digital photographs
-
Satellite images
-
Radiological images (x-rays, mammograms)
-
Binary images, fax images, engineering drawings
Sampling and Quantization
To create a digital image, we need to convert the continuous sensed data into digital form. This involves two processes: sampling and quantization. A continuous image, f(x, y), that we want to convert to digital form. An image may be continuous with respect to the x- and y-coordinates, and also in amplitude. To convert it to digital form, we have to sample the function in both coordinates and in amplitude.
Digitizing the coordinate values is called Sampling.
Digitizing the amplitude values is called Quantization.

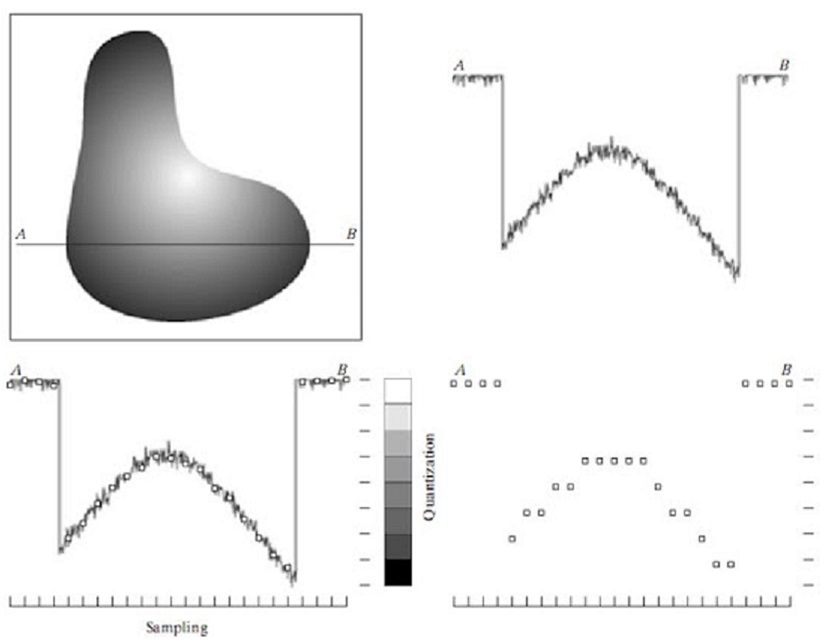
Figure: Analog Image and Digital Image
Free online Tutorial, Free Online Notes, Digital Image Processing, Sampling and Quantization, DIP, Computer Vision, Analysis, Fundamental Steps, Image acquisition, Image Enhancement, Image restoration, Segmentation, Recognition, Components of an Image Processing System Elements of Visual Perception, Image Formation in the Eye, Dilation and Erosion, Opening and Closing, Noise, Noise, Pattern Recognition, Compression, Image compression, Lossy compression, Lossless compression
Digital Image Processing
DIP notes
DIP University Notes VTU AKTU
Digital Image Processing pdf
Digital Image Processing pdf notes
Digital Image Processing short notes
Digital Image Processing question paper
Digital Image Processing projects
Digital Image Processing projects using MATLAB
DIP Subject Notes PDF
Digital Image Processing Lecture Notes PDF