Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing steps are divided into two categories. First where the input and output of the step are an image and second where the input to a step is an image but the output is attributes of the image. The Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing are shown in the following figure.
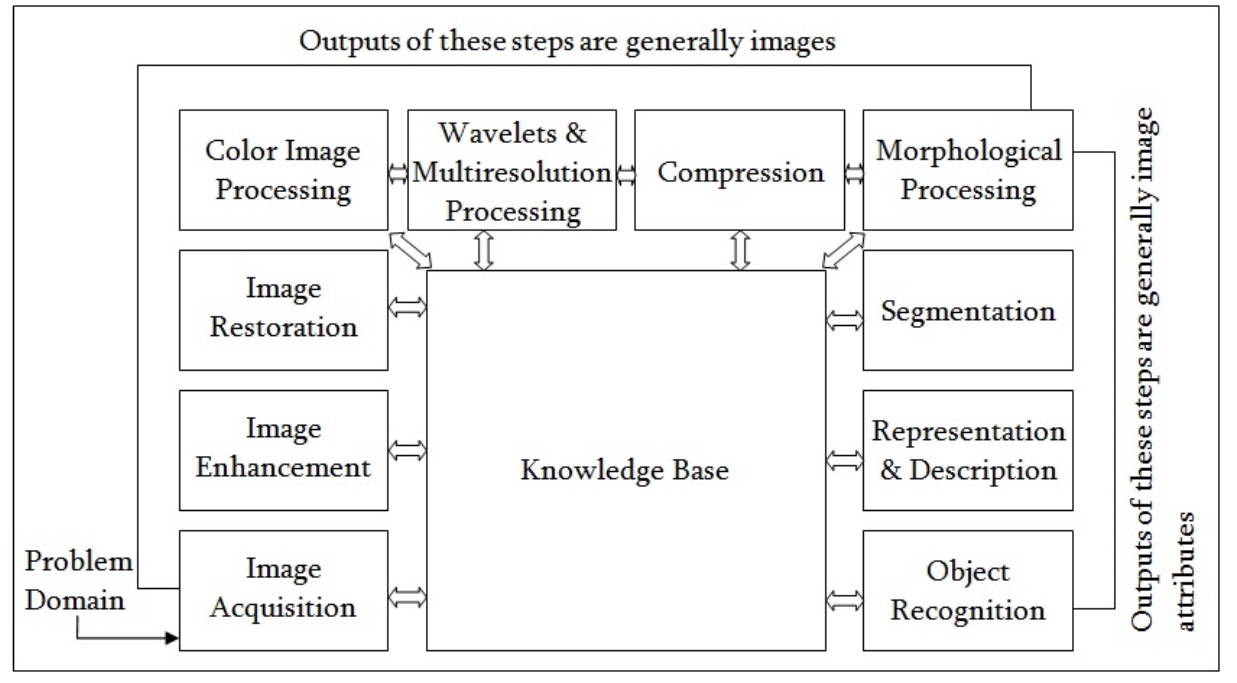
Figure: Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing
Image acquisition is the first stage of any vision system. After the image has been got, various methods of processing can be applied to the image to perform the many different vision tasks required today. However, if the image has not been acquired satisfactorily then the intended tasks may not be achievable, even with the aid of some form of image enhancement. The image acquisition stage involves pre-processing, such as scaling.
Image enhancement is one of the simplest and most interesting elements of digital image processing. The basic idea behind enhancement techniques is to either highlight specific features of interest in an image or reveal hidden detail. An everyday example of enhancement is when we increase an image's contrast because "it looks better." It's essential to remember that the area of image processing known as enhancement is highly subjective.
Image restoration is objective, in contrast to enhancement, which is subjective because restoration techniques typically are based on mathematical or probabilistic models of image degradation. On the other hand, enhancement is based on subjective human preferences for what makes a "good" enhancement result.
Color image processing is an area that has been gaining importance because of the significant increase in the use of digital images over the Internet.
Segmentation procedures partition an image into its constituent parts or objects. In general, autonomous segmentation is one of the most difficult tasks in digital image processing. A rugged segmentation procedure brings the process a long way toward a successful solution of imaging problems that require objects to be identified individually. On the other hand, weak or erratic segmentation algorithms almost always guarantee eventual failure. In general, the more accurate the segmentation, the more likely recognition is to succeed.
Representation and Description almost always follow the output of the segmentation stage, which usually is raw pixel data, constituting either the boundary of a region or all the points in the region itself. In either case, converting the data to a form suitable for computer processing is necessary. The first decision that must be m represented as a boundary or appropriate when the focus is on external shape characteristics, such as corners and Boundary representation is inflections. Regional representation is appropriate when the focus is on internal properties, such as texture or skeletal shape. In some applications, complement each other. Choosing a representation is transforming raw data into a suitable form for subsequent computer processing.
Description, also called feature selection, deals with extracting attributes that result in some quantitative information of interest or are basic for differentiating one class of objects from another.
Recognition is the process that assigns a label (e.g., "vehicle") to an object based on its descriptors. We conclude our coverage of digital image processing with the development of methods for the recognition of individual objects.
Knowledge about a problem domain is coded into an image processing system in the form of a knowledge database. This knowledge may be as simple as detailing regions of an image where the information of interest is known to be located, thus limiting the search that has to be conducted in seeking that information.
Free online Tutorial, Free Online Notes, Digital Image Processing, DIP, Computer Vision, Analysis, Fundamental Steps, Image acquisition, Image Enhancement, Image restoration, Segmentation, Recognition, Components of an Image Processing System Elements of Visual Perception, Image Formation in the Eye, Dilation and Erosion, Opening and Closing, Noise, Noise, Pattern Recognition, Compression, Image compression, Lossy compression, Lossless compression
Digital Image Processing
DIP notes
DIP University Notes VTU AKTU
Digital Image Processing pdf
Digital Image Processing pdf notes
Digital Image Processing short notes
Digital Image Processing question paper
Digital Image Processing projects
Digital Image Processing projects using MATLAB
DIP Subject Notes PDF
Digital Image Processing Lecture Notes PDF