3 Layer Architecture
The most common and well-known structure is a three-layer architecture. The model's process flow follows the points listed below.
Sensors and physical devices are the core of this model.
• A sensor must transmit data via a network, which is the layer above the sensors.
• Finally, as the top layer, data is processed by some type of application.
This model is primarily used in the context of machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. The three layers of architecture denotes three different levels: perception, network, and application layer. The three layers and their functions are as follows:
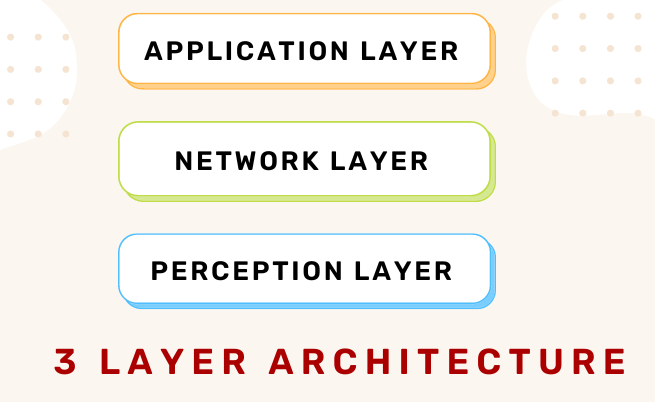
1: The perception layer is a physical layer, which has sensors for sensing and gathering information about the environment, is the perception layer. Sensors and embedded systems are primarily used in this. Based on the requirements, these collect large amounts of data. Edge devices, sensors, and actuators that communicate with their surroundings are also included. It detects some physical parameters or recognises other intelligent objects in the environment. This layer is responsible for data collection.
2. The Network Layer is responsible for the connecting other smart things, network devices, and servers. The information gathered by these devices must be distributed and saved. The network layer is in charge of this. It connects intelligent objects with other intelligent / smart objects. It is also responsible for data transfer. The network layer connects smart objects, network devices, and servers. Its capabilities are also used to transmit and process sensor data.
3. The Application Layer is responsible for providing the user with application-specific services. This application layer communicates with the user. It is in charge of providing software resources to the customer. In a smart home application, for example, users can activate a coffee machine by pressing a button in the app. It defines various applications for the Internet of Things, such as smart homes, smart cities, and smart health. The architecture can be used in a variety of applications due to the simple information flow between the layers. To turn on a smart air conditioner, for example, the user must open the app that is linked to it on their smartphone. The information will be transmitted to the device via the network layer, and after perceiving the temperature, the AC will be set to room temperature.